API Vulnerabilities: The "Back Doors" Through Which Your Applications Allow Hackers Access
We live in an interconnected world. Your online store automatically communicates with your bank for payments, your courier for deliveries, and your billing software. It all seems magical and fast. But have you ever wondered how these systems talk to each other?
They use digital “pipes” called APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). In 2026, API Vulnerabilities have become hackers’ favorite way to steal data en masse, precisely because they are often left unattended. At Altanet Craiova we consider API security a zero priority for any business that develops or uses modern software.
What is an API and why is it an easy target?
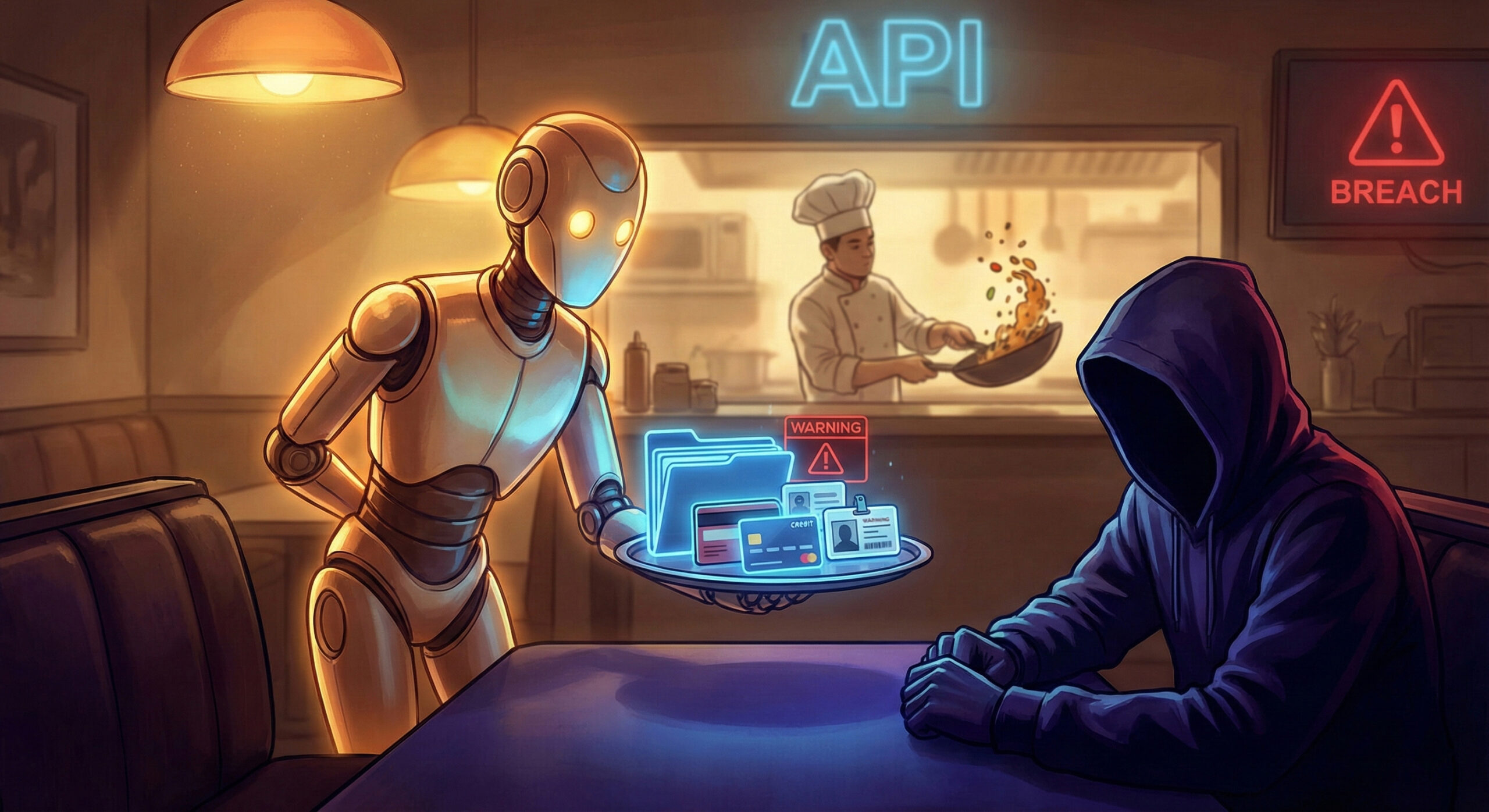
Think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant. You (the customer/phone app) sit at the table and ask the waiter (API) for the menu or food. The waiter goes to the kitchen (server/database), gets what you asked for, and brings it to you. You never go into the kitchen.
The problem arises when the "waiter" is not trained to check who is ordering the food. Vulnerabilities arise when hackers ask the waiter for things they shouldn't receive, and the waiter obediently brings them.
Examples of API attacks (BOLA)
The most common type of attack is called BOLA (Broken Object Level Authorization). Let's take a simple example:
- You are logged in to the courier application and want to see the status of your order with ID 1001.
- The application sends an API request: “Show me the details of order 1001”.
- The hacker intercepts the request and simply changes the number: “Show me the details of order 1002”, then 1003, 1004, etc.
- If the API is vulnerable, it doesn't check whether the hacker has the right to see the 1002 command, it just delivers it. This way, the attacker can download the entire database of addresses and names without cracking any passwords.
How do you secure your digital "doors"?
API security is not solved with a simple antivirus, but through strict programming and monitoring rules:
- Strict Authentication and Authorization: It is not enough for the user to be logged in. The API must check on each request: "Does this user have the right to see EXACTLY this document?".
- Rate Limiting: If someone requests details of 1000 orders in a minute, it is clearly an attack. The system should automatically block these excessive requests.
- Do not expose unnecessary data: Sometimes, the API sends the entire customer file (CNP, address, history) to the user's phone, even though the application only displays the name. Hackers can see this data hidden in the traffic. Send only the necessary information.
This topic is so critical that the global organization OWASP has a top dedicated exclusively to these risks. You can study the OWASP API Security Top 10 for technical details.
Conclusion
APIs are the engine of digital transformation, but they can also be your Achilles heel. Don't leave windows open to your database. Test your applications before hackers do.
Do you have a mobile application or an online store and want an API penetration test? Our team offers security auditing and specialized IT services. Visit our contact page and make sure your data remains private.
This material is part of Altanet's educational series on digital security. Want to know what other risks you are exposed to this year? See Complete list of cyber threats in 2026.

Leave a reply